


Next: Updating for the Gaussian
Up: Addition and multiplication nodes
Previous: Expectations
Form of the cost function
The form of the part of the cost function that an output of a node
affects is shown to be of the form
![$\displaystyle {\cal C}_p = M \left< \cdot \right> + V [(\left< \cdot \right>- \...
...rrent}})^2 + \mathrm{Var}\left\{\cdot\right\}] + E\left< \exp \cdot \right> + C$](img362.png) |
(61) |
where
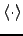 denotes the expectation of the quantity in
question. If the output is connected directly to another variable,
this can be seen from Eq. (10) by substituting
denotes the expectation of the quantity in
question. If the output is connected directly to another variable,
this can be seen from Eq. (10) by substituting
If the output is
connected to multiple variables, the sum of the affected costs is of
the same form. Now one has to prove that this form remains the same
when the signals are fed through the addition and multiplication
nodes. 5
If the cost function is of the predefined form (61)
for the sum 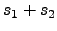 , it has the same form for
, it has the same form for 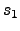 , when
, when 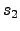 is regarded as a constant. This can be
shown using Eqs. (20), (21), and
(22):
is regarded as a constant. This can be
shown using Eqs. (20), (21), and
(22):
It can also be seen from (62) that when 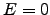 for
the sum
for
the sum 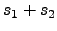 , it is zero for the addend
, it is zero for the addend 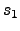 , that is
, that is
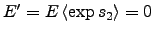 . This means that the outputs of
product and nonlinear nodes can be fed through addition nodes.
. This means that the outputs of
product and nonlinear nodes can be fed through addition nodes.
If the cost function is of the predefined form (61)
with 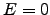 for the product
for the product 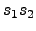 , it is similar for the variable
, it is similar for the variable 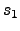 ,
when the variable
,
when the variable 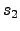 is regarded as a constant. This can be shown
using Eqs. (23) and (24):
is regarded as a constant. This can be shown
using Eqs. (23) and (24):



Next: Updating for the Gaussian
Up: Addition and multiplication nodes
Previous: Expectations
Tapani Raiko
2006-08-28
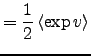
![$\displaystyle =\frac{1}{2}\left[\left< \exp v \right>\left(\mathrm{Var}\left\{m...
...^2-\left< s \right>_{\text{current}}^2\right)-\left< v \right>+\ln 2\pi\right].$](img370.png)
![]() , it has the same form for
, it has the same form for ![]() , when
, when ![]() is regarded as a constant. This can be
shown using Eqs. (20), (21), and
(22):
is regarded as a constant. This can be
shown using Eqs. (20), (21), and
(22):
![]() for the product
for the product ![]() , it is similar for the variable
, it is similar for the variable ![]() ,
when the variable
,
when the variable ![]() is regarded as a constant. This can be shown
using Eqs. (23) and (24):
is regarded as a constant. This can be shown
using Eqs. (23) and (24):