

Next: Optimistic Inference Control (OIC)
Up: Control Schemes
Previous: Control Schemes
In direct control schemes, the neural network itself acts as the
controller. Many such schemes exists, including direct inverse
control, optimal control, and feedforward control [13].
Direct control can only mimic the control done in the data that
has been used for learning. It therefore requires examples of correct
control aiming at the same goal.
Equation (8) provides a prediction of the control signal
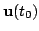 based on the previous control signal
based on the previous control signal
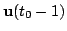 and the
previous estimate of the hidden state
and the
previous estimate of the hidden state
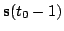 .
The prediction mapping is called the policy in Figure 1.
A control method that we simply call direct
control (DC), chooses the control signal by collapsing the inferred probability
distribution
.
The prediction mapping is called the policy in Figure 1.
A control method that we simply call direct
control (DC), chooses the control signal by collapsing the inferred probability
distribution
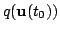 to its expected value.
When the control signal
to its expected value.
When the control signal
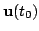 is selected and the observation
is selected and the observation
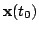 is made, the two
probability distribution collapse and these changes affect the
estimates of the states
is made, the two
probability distribution collapse and these changes affect the
estimates of the states
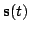 that are then re-inferred.
This works as the error feedback mechanism.
that are then re-inferred.
This works as the error feedback mechanism.
Tapani Raiko
2005-05-23