

Next: Simulation
Up: Experiments
Previous: Experiments
The Cart-Pole system [8] is a classic benchmark for nonlinear
control. The system consist of a pole (which acts as an inverted pendulum)
attached to a cart (Figure 3). The force applied to the cart
can be controlled, and the goal is to swing the pole to an upward position and
stabilise it. This must be accomplished without the cart crashing into the
walls of the track. Note that a linear controller cannot perform the swing-up.
The observed variables of the system are the position of the cart 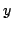 ,
angle of the pole measured from the upward position
,
angle of the pole measured from the upward position 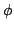 , and
their first derivatives
, and
their first derivatives 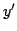 and
and 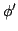 . Control input is the
force
. Control input is the
force 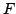 applied to the cart. The detailed dynamics and constraints for the
simulated cart-pole system can be found in [8].
applied to the cart. The detailed dynamics and constraints for the
simulated cart-pole system can be found in [8].
Figure 3:
The cart-pole system
[cc][cc] 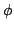
|
A discrete
system was simulated with a time step of
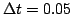 s. The possible force
was constrained between
s. The possible force
was constrained between
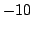 N and
N and
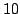 N, and the position between
N, and the position between
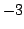 m and
m and
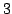 m.
The system was initialised to a
random state around
m.
The system was initialised to a
random state around
![$ [y,y',\phi,\phi']=[0,0,-\pi,0]$](img74.gif) with a standard
deviation of 0.1 for all the observed variables.
with a standard
deviation of 0.1 for all the observed variables.


Next: Simulation
Up: Experiments
Previous: Experiments
Tapani Raiko
2005-05-23