


Next: Projection pursuit.
Up: Linear projection methods
Previous: Linear projection methods
(PCA) [Hotelling, 1933] can be used to display the data as a linear
projection on such a subspace of the original data space that best preserves
the variance in the data. It is a standard method in data analysis; it
is well understood, and effective algorithms exist for computing the
projection. Even neural algorithms exist
[Oja, 1983, Oja, 1992, Rubner and Tavan, 1989, Cichocki and Unbehauen, 1993]. A demonstration of PCA is
presented in Figure 2.
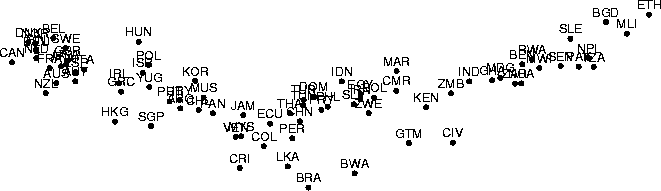
Figure: A dataset projected linearly onto the two-dimensional subspace
obtained with PCA. Each 39-dimensional data item describes different
aspects of the welfare and poverty of one country. The data set
consisting of 77 countries, used also in
Publication 2, was picked up from the World
Development Report published by the World Bank
(1992). Missing data values were neglected when
computing the principal components, and zeroed when forming the
projections. A key to the abbreviated country names is given in the
Appendix.
Sami Kaski
Mon Mar 31 23:43:35 EET DST 1997
