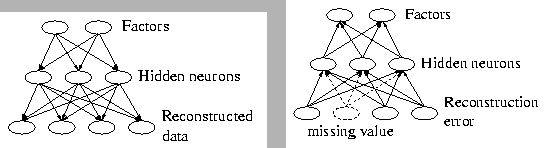
For efficiency reasons in Matlab code, the data elements, that are missing, are set to any value (e.g. zero) and the fact that they are missing is otherwise taken account of.
The approximation
![]() is assumed to be a
Gaussian density with a diagonal covariance matrix. This simplifies
the cost function
CKL given by (7) into
expectations of many simple terms. The terms concerning the
reconstruction error of the missing values are not included in the
cost function.
is assumed to be a
Gaussian density with a diagonal covariance matrix. This simplifies
the cost function
CKL given by (7) into
expectations of many simple terms. The terms concerning the
reconstruction error of the missing values are not included in the
cost function.
The partial derivatives of
CKL with respect to parameters
![]() are used for adaptation of
are used for adaptation of
![]() .
The effect of
i(t) on
CKL is transferred through
the noise vectors
e(t) which are also the reconstruction
errors as seen in formula (3). When the variance of
noise for the missing elements is set to infinity, the algorithm
effectively ignores the reconstruction errors of the missing values.
.
The effect of
i(t) on
CKL is transferred through
the noise vectors
e(t) which are also the reconstruction
errors as seen in formula (3). When the variance of
noise for the missing elements is set to infinity, the algorithm
effectively ignores the reconstruction errors of the missing values.
The reconstruction of data is obtained by the mapping f from the estimated factors. There is an analogy with the SOM. Factor vector scorresponds to the winning map unit in the SOM and f(s)corresponds to the model vector of the winner.
 |