



Next: Derivations
Up: Master's Thesis
Previous: Discussion
References
- Abut, 1990
-
Abut, H., editor (1990).
Vector Quantization.
IEEE Press, New York.
- Atkinson, 1989
-
Atkinson, K. E. (1989).
An Introduction to Numerical Analysis.
John Wiley & Sons, New York,
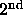 edition.
edition.
- Attneave, 1954
-
Attneave, F. (1954).
Informational aspects of visual perception.
Psychol. Rev., 61:183-193.
- Baddeley, 1996
-
Baddeley, R. (1996).
Searching for filters with ``interesting'' output distributions:
an uninteresting direction to explore?
Network, 7(2):409-421.
- Barlow, 1960
-
Barlow, H. B. (1960).
The coding of sensory messages.
In Thorpe, W. H. and Zangwill, O. L., editors, Current Problems
in Animal Behaviour, pages 331-360.
Cambridge University Press, Cambridge.
- Barlow, 1985
-
Barlow, H. B. (1985).
Cerebral cortex as model builder.
In Rose, D. and Dobson, V. G., editors, Models of the visual
cortex, pages 37-46. Wiley,
Chichester.
- Dayan and Zemel, 1995
-
Dayan, P. and
Zemel, R. S. (1995).
Competition and multiple cause models.
Neural Computation, 7(3):565-579.
- Field, 1994
-
Field, D. J. (1994).
What is the goal of sensory coding?
Neural Computation, 6(4):559-601.
- Földiák, 1990
-
Földiák, P. (1990).
Forming sparse representations by local anti-Hebbian learning.
Biological Cybernetics, 64:165-170.
- Földiák and Young, 1995
-
Földiák, P. and
Young, M. P. (1995).
Sparse coding in the primate cortex.
In Arbib, M. A., editor,
The Handbook of Brain Theory and Neural Networks,
pages 895-898. The MIT Press, Cambridge, Massachusetts.
- Haykin, 1994
-
Haykin, S. (1994).
Neural Networks.
Macmillan College Publishing Company, New York.
- Hinton et al., 1986
-
Hinton, G. E.,
McClelland, J. L., and
Rumelhart, D. E. (1986).
Distributed representations.
In Rumelhart, D. E., McClelland, J. L., and the PDP Research Group,
editors, Parallel Distributed Processing: Explorations in the
Microstructure of Cognition, Volume 1: Foundations, pages 77-109. The MIT
Press, Cambridge, Massachusetts.
- Hinton and Zemel, 1994
-
Hinton, G. E. and
Zemel, R. S. (1994).
Autoencoders, minimum description length and Helmholtz free energy.
In Cowan, J. D., Tesauro, G., and Alspector, J., editors,
Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 6, pages 3-10. Morgan
Kaufmann Publishers, San Francisco.
- Hodges et al., 1992
-
Hodges, J., Salmon, D., and Butters, N. (1992).
Semantic memory impairments in Alzheimer's disease.
Neuropsychologia, 30:301-314.
- Kohonen, 1995
-
Kohonen, T. (1995).
Self-Organizing Maps.
Springer-Verlag, Berlin-Heidelberg-New York.
- Meunier and Nadal, 1995
-
Meunier, C. and
Nadal, J.-P. (1995).
Sparsely coded neural networks.
In Arbib, M. A., editor,
The Handbook of Brain Theory and Neural Networks,
pages 899-901. The MIT Press, Cambridge, Massachusetts.
- Newsome et al., 1989
-
Newsome, W. T.,
Britten,
K. H., and Movshon, J. A. (1989).
Neuronal correlates of a perceptual decision.
Nature, 341:52-54.
- Oja, 1995
-
Oja, E. (1995).
Principal component analysis.
In Arbib, M. A., editor,
The Handbook of Brain Theory and Neural Networks,
pages 753-756. The MIT Press, Cambridge, Massachusetts.
- Olshausen and Field, 1995
-
Olshausen, B. A. and Field, D. J. (1995).
Sparse coding of natural images produces localized, oriented, bandpass
receptive fields. Technical Report CCN-110-95, Department of Psychology,
Cornell University, Ithaca, New York 14853.
- Ritter and Schulten, 1986
-
Ritter, H. and Schulten, K. (1986).
On
the stationary state of Kohonen's self-organizing sensory mapping.
Biological Cybernetics, 54:99-106.
- Rumelhart and Zipser, 1986
-
Rumelhart,
D. E. and Zipser, D. (1986).
Feature discovery by competitive learning.
In Rumelhart, D. E., McClelland, J. L., and the PDP Research Group,
editors, Parallel Distributed Processing: Explorations in the
Microstructure of cognition, Volume 1: Foundations, pages 151-193. The
MIT Press, Cambridge, Massachusetts.
- Salzman and Newsome, 1994
-
Salzman, C. D. and
Newsome, W. T. (1994).
Neural mechanisms for forming a perceptual decision.
Science, 264:231-237.
- Saund, 1994
-
Saund, E. (1994).
Unsupervised learning of mixtures of multiple causes in binary data.
In Cowan, J. D., Tesauro, G., and Alspector, J., editors,
Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 6, pages 27-31. Morgan
Kaufmann Publishers, San Francisco.
- Saund, 1995
-
Saund, E. (1995).
A multiple cause mixture model for unsupervised learning.
Neural Computation, 7(1):51-71.
- Schmidhuber, 1992
-
Schmidhuber, J. (1992).
Learning factorial codes by predictability minimization.
Neural Computation, 4(6):863-879.
- Sirosh, 1995
-
Sirosh, J. (1995).
A Self-Organizing Neural Network Model Of The Primary Visual
Cortex.
PhD thesis, University of Texas at Austin.
- Sirosh and Miikkulainen, 1994
-
Sirosh, J. and Miikkulainen, R. (1994).
Cooperative self-organization of afferent and lateral connections in
cortical maps.
Biological Cybernetics,
71(1):65-78.
- Thorpe, 1995
-
Thorpe, S. (1995).
Localized versus distributed representations.
In Arbib, M. A., editor,
The Handbook of Brain Theory and Neural Networks,
pages 549-552. The MIT Press, Cambridge, Massachusetts.
- Watanabe, 1981
-
Watanabe, S. (1981).
Pattern recognition as a quest for minimum entropy.
Pattern Recognition, 13:381-387.
- Zemel, 1993
-
Zemel, R. S. (1993).
A minimum description length framework for unsupervised
learning.
PhD thesis, University of Toronto, Canada.
Harri Lappalainen
Thu May 9 14:06:29 DST 1996