|
ASSOM | Adaptive-subspace self-organizing map |
|
DSS | Decision support system |
|
EEG | Electroencephalogram |
|
EM | Expectation maximization |
|
GNP | Gross national product |
|
GTM | Generative topographic mapping |
|
IR | Information retrieval |
|
KDD | Knowledge discovery in databases |
|
MDS | Multidimensional scaling |
|
PCA | Principal component analysis |
|
RBF | Radial basis function |
|
SOM | Self-organizing map |
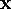 , , 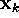 | input vector (data item), kth input vector |
|
t | discrete time index |
|
N | number of input vectors |
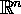 | input space; n-dimensional Euclidean space |
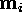 | ith cluster centroid, ith model vector |
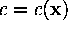 | index of the centroid
(or model vector) |
|
| that is closest to 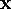 |
|
K | number of cluster centroids (and reference vectors) |
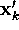 | projection of 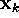 |
|
d(k,l) | distance between 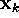 and and 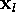 |
|
d'(k,l) | distance between 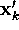 and and 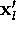 |
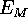 | cost function of the metric MDS method |
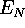 | cost function of the nonmetric MDS method |
|
f | a monotonically increasing function used in |
|
| nonmetric MDS |
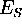 | cost function of Sammon's mapping |
|
q | inherent dimensionality of the data |
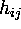 | neighborhood kernel in the SOM algorithm |
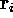 | location of the ith map unit on the map grid |
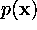 | probability density function of 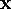 |
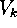 | Voronoi-region corresponding to 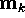 , viz. the set , viz. the set |
|
| consisting of those x for which 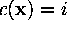 |
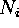 | number of data items in 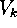 |
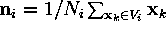 | centroid of 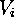 |
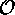 | computational complexity (``of the order of'') |
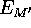 | a modified cost function of the metric MDS method |
|
F | a decreasing weighting function
|