 |
 |
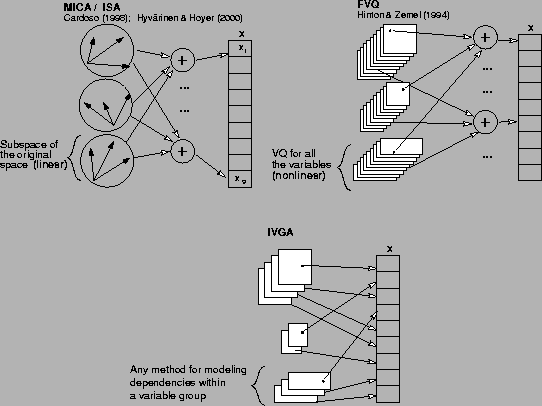
In multidimensional independent component analysis (MICA) [1], and its subsequent development independent subspace analysis (ISA) [4], the idea is to find independent linear feature subspaces that can be used to reconstruct the data efficiently. Thus each subspace is able to model the linear dependences in terms of the latent directions defining the subspace. The approach bears resemblance to IVGA which can be seen as a nonlinear version of MICA with the additional requirement which restricts the subspaces to be spanned by subsets of the variable axes.
Factorial vector quantization (FVQ)
[3,7] can be seen as a nonlinear
version of MICA. It uses several different VQs that cooperate to
reconstruct the observations and is thus very similar to
![]() .
The
structural differences of the FVQ model compared to the
.
The
structural differences of the FVQ model compared to the
![]() model
are: in FVQ (1) each vector in each pool or group contains all
the components (variables) of the original input vector, and (2) these
are summed to produce the value of a single output. In contrast, in
model
are: in FVQ (1) each vector in each pool or group contains all
the components (variables) of the original input vector, and (2) these
are summed to produce the value of a single output. In contrast, in
![]() each variable group is modeled by exactly one vector quantizer
(VQ). This leads to efficient computation as each VQ can operate
independently as opposed to FVQ where the winners are found
iteratively.
each variable group is modeled by exactly one vector quantizer
(VQ). This leads to efficient computation as each VQ can operate
independently as opposed to FVQ where the winners are found
iteratively.
Figure 1 illustrates the model structures of MICA/ISA, FVQ, and IVGA.