

Next: Diagonal Gaussian ensemble
Up: Ensemble Learning for Independent
Previous: Model selection
The measurements vectors 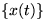 are assumed to be generated by a
linear mapping A from mutually independent source signals
are assumed to be generated by a
linear mapping A from mutually independent source signals 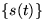 and additive Gaussian noise
and additive Gaussian noise 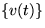 .
.
x(t) = As(t) + v(t)
The components vi(t) of the noise are assumed to have means bi
and variances 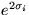 . Another way to put this is to say
that x(t) has Gaussian distribution with mean As(t)+b and diagonal
covariance with components
. Another way to put this is to say
that x(t) has Gaussian distribution with mean As(t)+b and diagonal
covariance with components 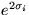 . Each component Aij
of the linear mapping is assumed to have zero mean and unit variance.
. Each component Aij
of the linear mapping is assumed to have zero mean and unit variance.
The distribution of each source signal is a mixture of Gaussians (MOG).
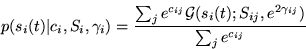
The parameters cij are the logarithms of mixture coefficients,
S the means and 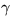 the logarithms of the standard deviations
of the Gaussians
the logarithms of the standard deviations
of the Gaussians![[*]](foot_motif.gif) (here
(here 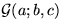 denotes a Gaussian distribution over a with mean b and
variance c).
denotes a Gaussian distribution over a with mean b and
variance c).
The distributions of parameters cij, Sij, 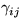 ,bi and
,bi and 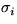 are
are 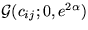 ,
,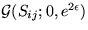 ,
, 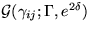 ,
,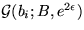 and
and 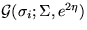 .
.
The prior distribution of the hyperparameters 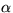 ,
, 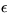 ,
,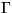 ,
, 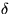 , B,
, B, 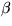 ,
, 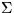 and
and 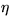 is assumed to
be uniform in the area of reasonable values for the hyperparameters.
is assumed to
be uniform in the area of reasonable values for the hyperparameters.
To summarise: the eight hyperparameters are assigned flat prior pdfs.
The distributions of other parameters are defined hierarchically from
these using Gaussian distributions each parametrised by the mean and
the logarithm of the standard deviation. The joint pdf of 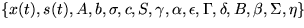 is simply the product of the independent pdfs.
is simply the product of the independent pdfs.


Next: Diagonal Gaussian ensemble
Up: Ensemble Learning for Independent
Previous: Model selection
Harri Lappalainen
7/10/1998
![]()
![[*]](foot_motif.gif) (here
(here ![]() ,bi and
,bi and ![]() are
are ![]() ,
,![]() ,
, ![]() ,
,![]() and
and ![]() .
.![]() ,
, ![]() ,
,![]() ,
, ![]() , B,
, B, ![]() ,
, ![]() and
and ![]() is assumed to
be uniform in the area of reasonable values for the hyperparameters.
is assumed to
be uniform in the area of reasonable values for the hyperparameters.
![]() is simply the product of the independent pdfs.
is simply the product of the independent pdfs.