


Next: CONJUGATE GRADIENT METHODS
Up: OPTIMIZATION ALGORITHMS ON RIEMANNIAN
Previous: OPTIMIZATION ALGORITHMS ON RIEMANNIAN
The natural gradient learning algorithm is analogous to conventional
gradient ascent algorithm and is given by the iteration
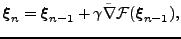 |
(17) |
where the step size 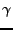 can either be adjusted adaptively during
learning or computed for each iteration using e.g. line
search (Amari, 1998). This line search should be performed or any
longer step taken along a suitable geodesic, which is a length
minimizing curve and therefore the Riemannian counterpart of a
straight line. In practice, geodesics are often approximated with straight
lines (Amari, 1998), as natural gradient ascent is typically applied to
problems with
complex geometries, and the geodesics on such manifolds
can be hard to derive and compute.
can either be adjusted adaptively during
learning or computed for each iteration using e.g. line
search (Amari, 1998). This line search should be performed or any
longer step taken along a suitable geodesic, which is a length
minimizing curve and therefore the Riemannian counterpart of a
straight line. In practice, geodesics are often approximated with straight
lines (Amari, 1998), as natural gradient ascent is typically applied to
problems with
complex geometries, and the geodesics on such manifolds
can be hard to derive and compute.
In general, the performance of natural gradient learning is superior
to conventional gradient learning when the problem space
is Riemannian.
For instance, natural gradient learning
can often avoid the plateaus present in conventional gradient
learning (Amari, 1998).
Tapani Raiko
2007-04-18